Effective and Marginal Tax: Understanding the difference

The tax code contains several terms we rarely use in everyday conversation. Two of the more common are Marginal Tax Rates and Effective Tax Rates. Knowing what they mean can help you think differently about your potential tax obligation.
Definitions of Effective and Marginal Tax
Marginal Tax Rate: This is the tax rate applied to the next dollar you earn. Our income tax rates are progressive. So, the next dollar you earn could be taxed at as little as zero or as high as 37%!
Effective Tax Rate: This is the tax rate you actually pay. It is the total taxes paid divided by your total taxable income. In other words, after taking your income and then applying taxes, deductions, credits, exemptions, and other adjustments, you have your actual tax obligation. This obligation is a percent of your income.
A Simple Example
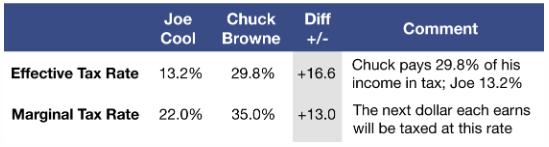
Consider two single people; Joe Cool who earns $50,000 and Chuck Browne who earns $500,000. If we had a flat tax of 10%, Mr. Cool would pay $5,000 in tax and Mr. Browne would pay $50,000 in tax. Both of their Effective Tax Rates would be 10%. Their Marginal Tax Rates would also be 10% because each additional dollar would be taxed at the same 10%. However, it is a different picture when you apply our progressive tax rates.
If we use the 2022 U.S. tax table for a single filer, Joe Cool pays $6,617 and Chuck Browne pays $148,753 in federal tax. This is because tax rates applied to Joe Cool’s income are (10-22%) while Chuck’s income over $50,000 gets Marginal Tax Rates of (22-35%). Ignoring other tax factors, our two taxpayers’ tax rates are:
Why Care?
- Calculating Returns. The actual return you receive on any taxable investment will be determined by your Marginal Tax Rate. A $500 profit from a new investment could cost Joe Cool 15% in federal tax, but it could cost Chuck Browne 35% in federal tax.
- Phaseouts can provide a dramatic impact on Effective Tax Rates. The simple examples above do not account for income limits applied to many tax benefits. Additional income could dramatically impact Joe Cool if it triggers losing things like an Earned Income Credit, or Child Tax Credit. This could increase Joe’s Effective Tax Rate while not touching his Marginal Tax Rate.
- Extra work can help the taxman more than you. There have been cases where adding a second job can cost you money by not understanding the impact of the income on your Effective Tax Rate. This is especially true for retired workers receiving Social Security Retirement Benefits. That extra job may make your Social Security benefits taxable.
- It’s not that simple. In addition to all the different income phase-outs for credits and deductions, your Effective Tax Rate could be impacted by eliminating itemized deductions, the Alternative Minimum Tax, and the marriage penalty.
Look at last year’s tax return and calculate your Effective Tax Rate. Then, look at your income. Next, determine the Marginal Tax Rate applicable to your next dollar of income. Finally, if you anticipate an increase in earnings, consider forecasting the impact on your Effective Tax Rate. Contact our RRBB accountants and advisors for more information or if you have any questions.
© 2022
RRBB eNEWSLETTER
Get free tax planning and financial advice




